
Testing and Results
The group performed three tests on the array in order to determine the success of vibration damping techniques. The three tests are as follows: DC Motor Test, Base Impact Test, Rod Impact Test.
DC Motor Test

Purpose:
The DC Motor Test was conducted to characterize the vibration propagation caused by the RDS Robot's DC Motors.
Results: The results of the DC Motor Test as as shown below:
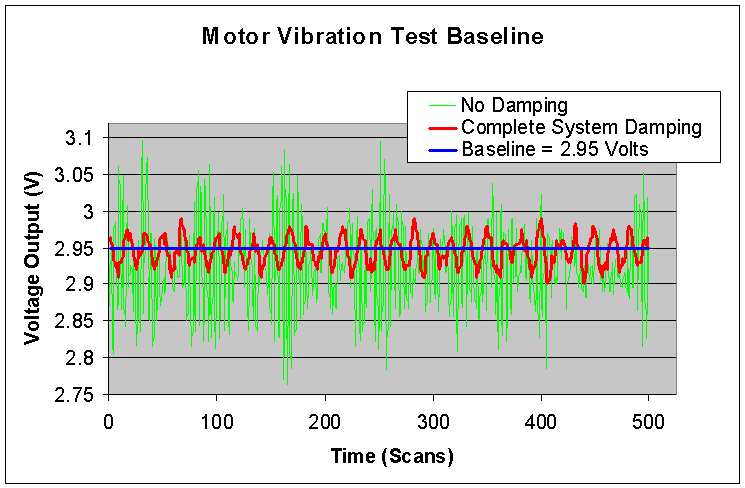

Results Discussion:
The major goal for the DC Motor Test was achieved in that the shock impulse magnitude was reduced by 74%, meaning that less shock energy is causing a disturbance in the microphone sensors. This is evident also in the excitation of the microphone sensors being reduced by 76.5%, meaning that less interference will be inherent in the acoustic eye sensor during RDS navigation.
Rod Impact Test

The rod is impacted by utilizing the pendulum swing shown above, and 4 ounce weights to impact the rods at the markings shown below:

Purpose:
The purpose of the rod impact test was to characterize the effects of vibration from direct impact of the ABS extension rods into an obstruction during RDS navigation.
Results:
The results of the rod impact test are as follows:
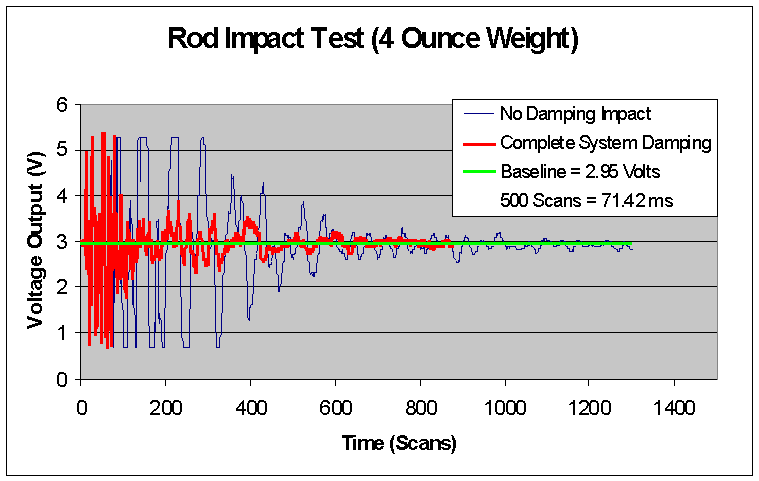
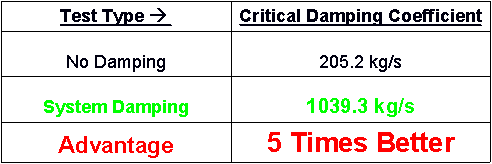
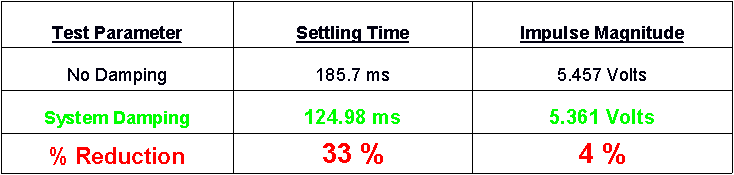
Results Discussion:
As shown above, the critical damping coefficient was increased 5 fold over the non-damped case. This means that the complete damped system will mitigate vibration propagation faster than the original set-up that Eglin AFRL was utilizing for their acoustic array housing. Also, the settling time was reduced by 33% over the original set-up. This shows that the microphone sensors will be affected over a shorter period of time translating into more navigation capabilities for the RDS, with less interference.
Base Impact Test
The final test that was conducted was a base impact test, shown below:

Purpose:
The purpose of the base impact test was to characterize the effects of vibration from direct impact of the array base into an impact during RDS navigation.
Results:
The graphical and tabular results of the base impact test are shown below:
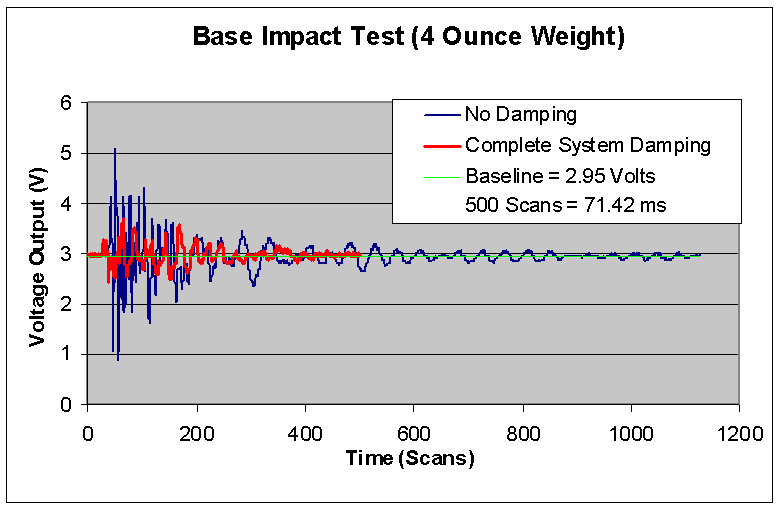
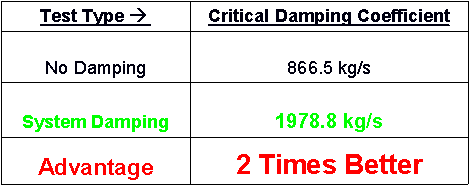
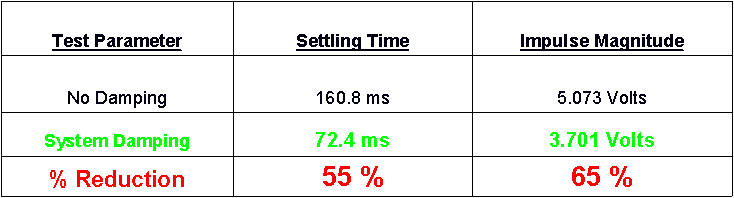
Results Discussion:
From the table above, the critical damping coefficient more than doubled over the coefficient found when using the original set-up. This shows that our vibration damping techniques significantly slowed the vibration propagation through our array. Also, the settling time was reduced by 55%, and the impulse magnitude was decreased by 65%. These results depict a major reduction in vibration reaching the microphone sensors compared to the original set-up obtained from Eglin.