


|
Concept Generation |
|
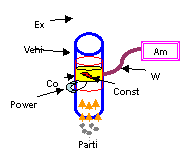
Concept Electrical conductivity is a measure of how well a material accommodates the transport of electric charge: ∑ A conductor such as a metal has high conductivity. ∑ An insulator like glass or a vacuum has low conductivity. ∑ The conductivity of a semiconductor is generally intermediate, but varies widely under different conditions, such as exposure of the material to electric fields or certain frequencies of light. Ohmís Law can be used to describe conductivity voltage is equal to the product of the current applied and the resistance, V=I*R. The electrical conductivity (s) is described by the equation ††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† Where r is the resisitivity. By applying a constant voltage to the filter and knowing the resistance caused by the cordierite in the filter, one can determine the resulting current using the relation
with I being the resistance, V the voltage, and R the resistance. Once the filter begins to fill with soot and other particulates, the resistance caused by the filter will ultimately change as a result of the different electrical properties of the soot, specifically the charge mobility and the resistivity. †Previous Page††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† Continue |
Concept #4 |
|
Idea #4: Particulate Measurement through Electrical Current Analysis |
|
Click here for larger picture. |

|
Cummins |
|
Diesel Particulate Filter |
