Kinematics
refers to the motion of a particle without regard to what causes the motion.
Particles in a continuum refer to the infinitesimal volume of a body.
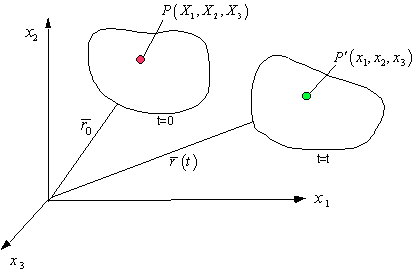
![]()

Particle
P at t=0 moves to Pí at t=t.
The position vector,
![]()
Every
particle moves according
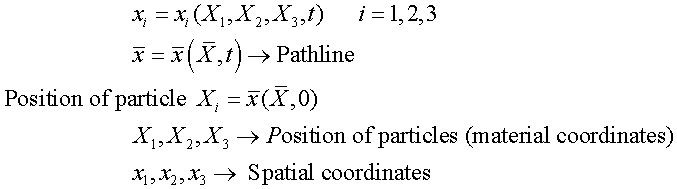
In
a reference configuration, we may use original particle description leading to a
Lagarangian description.
If we refer to current coordinates at t=t, then it is called Eulerian
description.