Recall
that
![]() , where
, where
![]() is the original vector between two
points, and
is the original vector between two
points, and
![]() the vector after deformation. If
the vector after deformation. If
![]() is a pure
is a pure
![]() , then
, then
![]() have same length, i.e., no strain but rigid body motion.
It is likely that in a body some parts are subjected to
pure strain, pure rotation, or a combination of the two. To compute the
strain, all the rigid motion effect should be eliminated.
have same length, i.e., no strain but rigid body motion.
It is likely that in a body some parts are subjected to
pure strain, pure rotation, or a combination of the two. To compute the
strain, all the rigid motion effect should be eliminated.
If
![]() is symmetric, let
is symmetric, let
![]() be designated as
be designated as
![]() , then
, then
![]()
In
the neighborhood of
![]() , there is only pure stretching. Since
, there is only pure stretching. Since
![]() is real and symmetric,
is real and symmetric,
![]() can be made diagonal with specific
can be made diagonal with specific
![]() corresponding to
corresponding to
![]() ,
,
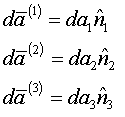
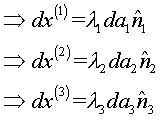
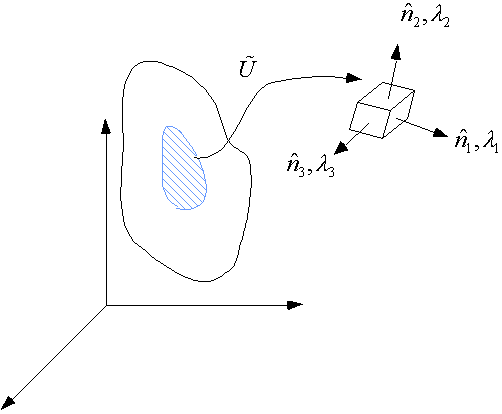
Let
stretch
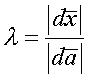
Thus
eigen values of
![]() are the principal stretches
(minimum, intermediate, maximum)
are the principal stretches
(minimum, intermediate, maximum)