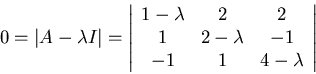
Eigenvalues:
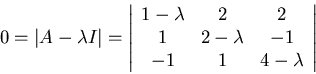
![]()
Eigenvectors corresponding to ![]() satisfy
satisfy
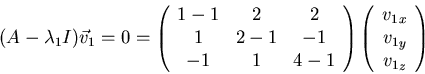
Solving using Gaussian elimination:
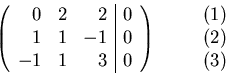
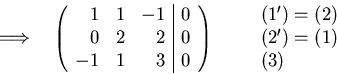
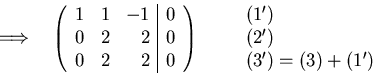
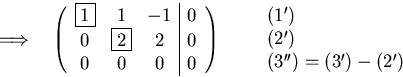
The general solution space is:
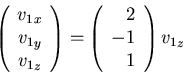
We choose v1z=1 to get
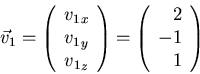
Eigenvectors corresponding to ![]() satisfy
satisfy
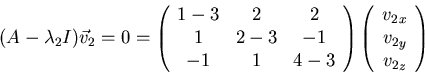
Solving using Gaussian elimination:
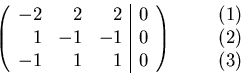
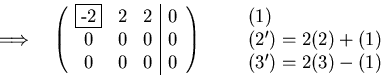
The general solution space is:
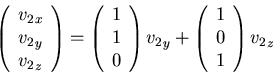
We can use the two vectors above, which means choosing v2y=1 and v2z=0 for one, and v2y=0 and v2z=1 for the other. That gives
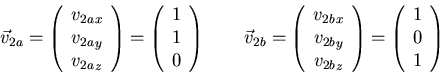
If the three vectors ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are
used as basis, A becomes diagonal. So despite the multiple root,
this A is still diagonalizable. But if the solution space for the
second eigenvalue would have been one-dimensional, the matrix would
not have been diagonalizable.
are
used as basis, A becomes diagonal. So despite the multiple root,
this A is still diagonalizable. But if the solution space for the
second eigenvalue would have been one-dimensional, the matrix would
not have been diagonalizable.