Eigenvalues:
Definition
A nonzero vector ![]() is an eigenvector of a matrix A if
is an eigenvector of a matrix A if ![]() is
a multiple of
is
a multiple of ![]() :
:
![]()
Graphically, if ![]() is an eigenvector of A, then the vector
is an eigenvector of A, then the vector
![]() is in the same (or exactly opposite direction) as
is in the same (or exactly opposite direction) as ![]() :
:
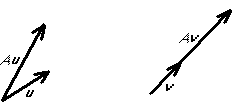
An eigenvector is indeterminate by a constant that must be chosen. Do not leave undetermined coefficients in eigenvectors.
Example
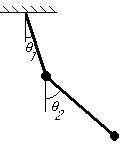
Equations of motion:
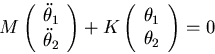
Setting ![]()
![]()
Premultiplying by M-1 and defining A=M-1K,
![]()
Try solutions of the form ![]() . The
constant vector
. The
constant vector ![]() determines the ``mode shape:''
determines the ``mode shape:''
![]() . The exponential gives the time-dependent
amplitude.
. The exponential gives the time-dependent
amplitude.
Plugging the assumed solution into the equations of motion:
![]()
There will be two different eigenvectors ![]() , hence two mode shapes
and two corresponding frequencies.
, hence two mode shapes
and two corresponding frequencies.
Note: we may lose symmetry in the above procedure. There are better ways to do this.
Procedure
To find the eigenvalues of a matrix A, first find the zeros of
the determinant ![]() :
:
![]()
When these eigenvalues are found, the corresponding eigenvectors
follow from solution of ![]() . We need to
choose one coefficient for each eigenvector arbitrarily.
. We need to
choose one coefficient for each eigenvector arbitrarily.