|
|
|
|
Next: 3 01/31 F |
|
Find the unit normal ![]() to the surface at P. Now assume that
the surface is reflective, satisfying Snell's law. An incoming
light beam parallel to the
to the surface at P. Now assume that
the surface is reflective, satisfying Snell's law. An incoming
light beam parallel to the ![]() -axis hits the surface at P. Find a
vector equation that describes the path of the reflected beam.
-axis hits the surface at P. Find a
vector equation that describes the path of the reflected beam.
Hint: let ![]() be a vector along the light ray. The component of
be a vector along the light ray. The component of ![]() in the direction of
in the direction of ![]() is
is ![]() . The component vector in the direction of
. The component vector in the direction of ![]() is defined as
is defined as ![]() . Sketch this
vector along with vector
. Sketch this
vector along with vector ![]() . In which direction is the
remainder
. In which direction is the
remainder ![]() ? Now figure out what
happens to
? Now figure out what
happens to ![]() and
and ![]() during the reflection. Take it
from there.
during the reflection. Take it
from there.
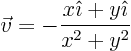
source strength,the amount of fluid created out of nothing. (A sink being a negative source, where fluid disappears into nothing.) So, what do you think of the value of the divergence of the point sink at the origin (assuming that you smooth out the singularity a bit)? Note: if the fluid is not incompressible, it is really volume flows you are comparing, not mass flows, and the divergence is a measure of the relative rate of specific volume expansion. Additional volume is created out of nothing, not mass.