Typical head loss values for important situations may be found in
tables. For bends and area changes, they can be expressed as
a head loss coefficient: ![]() .
.
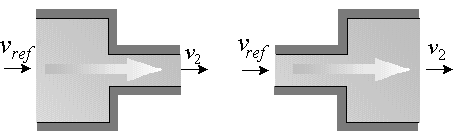
Exercise:
Why express the headloss in terms of? Why not, say,
?
For the developed two-dimensional duct flow in the previous subsection, the head loss over a distance L of the duct is:
![]()
![]()
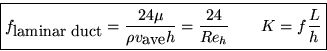

There will be an additional head loss for the entrance effects (called minor head loss):
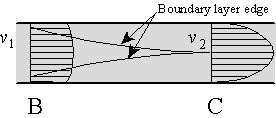
For the duct exit, the kinetic energy will probably be mostly lost:
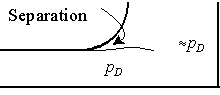
You should now be able to do 7.3 and 4