Next: Some Manipulations
Up: Introduction
Previous: Complex variables
Any differentiable complex function F(z) is the complex
potential for a 2D incompressible potential flow. Further 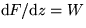 is the complex conjugate velocity.
is the complex conjugate velocity.
Reason: differentiability requires that 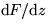 is the same
whichever direction we take
is the same
whichever direction we take 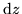 . In particular if we take
. In particular if we take 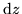 equal to a change
equal to a change 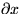 in x only, we should get the
same as when we take
in x only, we should get the
same as when we take 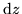 equal to a change
equal to a change 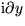 in
y only. That means, if
in
y only. That means, if 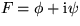 :
:
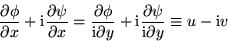
Since 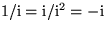 ,
,
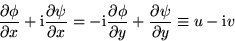
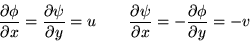
from which it follows that u and v satisfy both the continuity
equation and irrotationality:
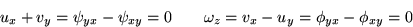
Differentiable complex functions are easy to find:
- Constants are differentiable:
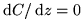 .
. - Function F(z)=z is differentiable:
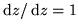 .
. - Sums of differentiable functions are differentiable (see your calculus
book.)
- Products of differentiable functions are differentiable (see
your calculus book.)
- Inverses of differentiable functions are differentiable (see
your calculus book.)
- Functions with converging Taylor series are differentiable.
Not differentiable:
- Purely real functions such as x,
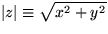 , ...
, ...
- Purely imaginary functions such as
 ,
, 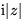 , ...
, ...
- Complex conjugates such as
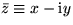 .
.
Exercise:
Give as many 2d incompressible potential flows as you can.
Exercise:
Do question 18.3 in the book.
Next: Some Manipulations
Up: Introduction
Previous: Complex variables
 02/28/00 0:20:11
02/28/00 0:20:11
 02/28/00 0:36:23
02/28/00 0:36:23
 03/01/00 0:01:35
03/01/00 0:01:35
 03/13/00 0:01:27
03/13/00 0:01:27
![]() is the complex conjugate velocity.
is the complex conjugate velocity.
![]() is the same
whichever direction we take
is the same
whichever direction we take ![]() . In particular if we take
. In particular if we take ![]() equal to a change
equal to a change ![]() in x only, we should get the
same as when we take
in x only, we should get the
same as when we take ![]() equal to a change
equal to a change ![]() in
y only. That means, if
in
y only. That means, if ![]() :
:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()