| Partial Differential Equations 0.15 alpha |
|
© Leon van Dommelen |
|
D.2 Some properties of harmonic functions
The mean value theorem says that if you take a sphere around some
point, the average of  on the surface of that sphere is the value
of
on the surface of that sphere is the value
of  at the center of the sphere. That is true as long
as
at the center of the sphere. That is true as long
as  satisfies the Laplace equation inside the sphere.
satisfies the Laplace equation inside the sphere.
To prove the mean value theorem, take the origin of your coordinate
system at the center of the sphere. Then integrate the Laplace
equation over the volume of a sphere. Use the divergence theorem to
get
But the normal direction is the radial direction, so
This holds for a spherical surface of any radius 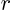 around the origin
as long as the Laplace equation is applicable in the sphere. Divide by
the total spherical surface:
around the origin
as long as the Laplace equation is applicable in the sphere. Divide by
the total spherical surface:
The ratio 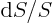 does not depend on the radius. So you can take
the derivative out of the integral to get
does not depend on the radius. So you can take
the derivative out of the integral to get
The integral is by definition the average of  on the spherical
surface. So it does not depend on the radius of the surface. That
means it remains the same when you let the radius of the spherica;
surface go to zero. But when
on the spherical
surface. So it does not depend on the radius of the surface. That
means it remains the same when you let the radius of the spherica;
surface go to zero. But when 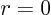 , you get the average of
, you get the average of  at the
origin, which is simply
at the
origin, which is simply  at the origin, since the origin is a
single point.
at the origin, since the origin is a
single point.
The minimum and maximum properties follow immediately from the mean
value theorem. Note that the minimum property implies the maximum
property: the maximum of a harmonic function  is the minimum
of the harmonic function
is the minimum
of the harmonic function 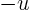 .
.
To show the minimum property, consider an arbitrary point in the
interior of the domain. Put a sphere of a sufficiently small radius
around the point; the sphere must stay in the domain. Now  is at
the considered point equals the average value of
is at
the considered point equals the average value of  on the spherical
surface. And an average is always in between the minimum and maximum
values. So
on the spherical
surface. And an average is always in between the minimum and maximum
values. So  at the considered point cannot be less than the
smallest
at the considered point cannot be less than the
smallest  value on the spherical surface. So
value on the spherical surface. So  at the considered
point cannot be a unique minimum, lower than all other
at the considered
point cannot be a unique minimum, lower than all other  values.
values.
You may wonder whether  might be a minimum that is not unique. But
for the average of
might be a minimum that is not unique. But
for the average of  on the spherical surface to equal the lowest
value of
on the spherical surface to equal the lowest
value of  requires that
requires that  is everywhere the lowest value on the
surface. If
is everywhere the lowest value on the
surface. If  would be above the minimum anywhere, the average
would be above the minimum. So any spherical surface around the
considered point has the same value of
would be above the minimum anywhere, the average
would be above the minimum. So any spherical surface around the
considered point has the same value of  as the considered point.
At least as long as the sphere stays inside the domain. In other
word,
as the considered point.
At least as long as the sphere stays inside the domain. In other
word,  is constant within some sphere around the considered point
that goes up to the boundary. And for every point inside that sphere
there is again a surrounding sphere in which
is constant within some sphere around the considered point
that goes up to the boundary. And for every point inside that sphere
there is again a surrounding sphere in which  is constant. You can
then readily see from a sketch that this means that
is constant. You can
then readily see from a sketch that this means that  will have to
the the minimum everywhere. In other words,
will have to
the the minimum everywhere. In other words,  must be a constant
for there to be a nonunique minimum in the interior of the region.
must be a constant
for there to be a nonunique minimum in the interior of the region.
![]() on the surface of that sphere is the value
of
on the surface of that sphere is the value
of ![]() at the center of the sphere. That is true as long
as
at the center of the sphere. That is true as long
as ![]() satisfies the Laplace equation inside the sphere.
satisfies the Laplace equation inside the sphere.
![]() is the minimum
of the harmonic function
is the minimum
of the harmonic function ![]() .
.
![]() is at
the considered point equals the average value of
is at
the considered point equals the average value of ![]() on the spherical
surface. And an average is always in between the minimum and maximum
values. So
on the spherical
surface. And an average is always in between the minimum and maximum
values. So ![]() at the considered point cannot be less than the
smallest
at the considered point cannot be less than the
smallest ![]() value on the spherical surface. So
value on the spherical surface. So ![]() at the considered
point cannot be a unique minimum, lower than all other
at the considered
point cannot be a unique minimum, lower than all other ![]() values.
values.
![]() might be a minimum that is not unique. But
for the average of
might be a minimum that is not unique. But
for the average of ![]() on the spherical surface to equal the lowest
value of
on the spherical surface to equal the lowest
value of ![]() requires that
requires that ![]() is everywhere the lowest value on the
surface. If
is everywhere the lowest value on the
surface. If ![]() would be above the minimum anywhere, the average
would be above the minimum. So any spherical surface around the
considered point has the same value of
would be above the minimum anywhere, the average
would be above the minimum. So any spherical surface around the
considered point has the same value of ![]() as the considered point.
At least as long as the sphere stays inside the domain. In other
word,
as the considered point.
At least as long as the sphere stays inside the domain. In other
word, ![]() is constant within some sphere around the considered point
that goes up to the boundary. And for every point inside that sphere
there is again a surrounding sphere in which
is constant within some sphere around the considered point
that goes up to the boundary. And for every point inside that sphere
there is again a surrounding sphere in which ![]() is constant. You can
then readily see from a sketch that this means that
is constant. You can
then readily see from a sketch that this means that ![]() will have to
the the minimum everywhere. In other words,
will have to
the the minimum everywhere. In other words, ![]() must be a constant
for there to be a nonunique minimum in the interior of the region.
must be a constant
for there to be a nonunique minimum in the interior of the region.