- 1.
- What output do you get from the statement:
cout << "H" << "el" << 'l' << 'o' << endl;
- 2.
- What output do you get from the statement:
cout << "0.500 = " << 0.500 << endl;
- 3.
- What is the difference in output between the program pieces on
the left and on the right:
cout << "Line 1$\backslash n$Line 2$\backslash n$"; cout << "Line 1$\backslash n$";
cout << "Line 2$\backslash n$";
- 4.
- What is the difference in output between the program pieces on
the left and on the right:
cout << "Line 1$\backslash n$"; cout << "Line 1" << endl
cout << "Line 2$\backslash n$"; << "Line 2" << endl;
- 5.
- What should you get from the statement:
cout << "\a" << "Hi" << endl << "there" << endl;
(Does not work on the PCs, but works on Unix.)
- 6.
- Why is the program on the right much better than the one on
the left:
#include <iostream.h> #include <iostream.h>
main ( ) { main ( ) {
int a; int a;
... int b;
int b; ...
... ...
a=1; a=1;
b=3; b=3;
cout << a+b << endl; cout << a+b << endl;
... ...
} }
(The dots stand for lots of other statements that are not important.)
- 7.
- What is obviously wrong (except lack of neatness):
#include <iostream.h>
main ( ) {
int pi;
...
pi = 3.141593;
...
return 0;
}
- 8.
- Why is the program on the left much better than the one on the
right:
#include <iostream.h> #include <iostream.h>
main ( ) { main ( ) {
float pi = 3.141593; float pi;
.... ....
.... pi=3.141593
.... ....
area = pi*r*r area = pi*r*r
.... ....
(The dots stand for lots of other statements that are not important.)
The size of the program (number of lines or number of characters)
is not an important consideration.
- 9.
- Why is the comment on the left much better than the one on
the right:
#include <iostream.h> #include <iostream.h>
main ( ) { main ( ) {
// Declarations: // Declarations:
// Define pi: float pi = 3.141593; // pi is defined
float pi = 3.141593; ....
.... ....
(The dots stand for lots of other statements that are not important.)
The size of the program (number of lines or number of characters)
is not an important consideration.
- 10.
- List at least four types of people that can benefit from the
comments that you put in your program? Why?
- (a)
-
- (b)
-
- (c)
-
- (d)
-
- 11.
- Can you store arbitrarily large integers in an int? In a long int?
- 12.
- Can you store arbitrarily large floating point numbers in a float?
In a double?
- 13.
- Can you store arbitrarily accurate floating point numbers such
as
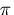 or
or 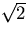 in a float? In a double?
in a float? In a double?
- 14.
- What do you get from:
cout << "3*3 = " << 3*3 << endl;
- 15.
- What do you get from:
float a; ...; a=1.5; cout << a << endl;
- 16.
- What do you get from, and why:
int a; ...; a=1.5; cout << a << endl;
- 17.
- What do you get from, and why:
cout << ".33 = " << 1/3 << endl;
- 18.
- What do you get from, and why:
cout << ".33 = " << 1./3 << endl;
- 19.
- What do you get from, and why:
cout << "Large: " << 300000*300000 << endl;
- 20.
- What do you get from, and why:
cout << "9 = " << 1+2*3 << endl;
- 21.
- What do you get from, and why:
cout << ".25 = " << 1./2.*2. << endl;
- 22.
- What do you get from, and why:
cout << "1 = " << 1./2./2. << endl;
- 23.
- What do you get from:
int i; ...; i=1; cout << i++; cout << i << endl;
- 24.
- What do you get from:
int i; ...; i=1; cout << ++i; cout << i << endl;
- 25.
- Explain what happens during the execution of:
int i,j; ...; cin >> i >> j;
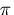 or
or 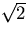 in a float? In a double?
in a float? In a double?