


Next: Logical Operators
Up: If Statement
Previous: Nested ifs
A common programming construct that is based upon nested ifs is the
if-else-if ladder. It looks like this

The conditional expressions are evaluated from the top downward. As soon as a true
condition is found, the statement associated with it is executed, and the rest of
the ladder is bypassed. If non of the conditions is true, then the final else
statement will be executed. The final else often acts as a default condition;
that is, if all other conditions tests fail, then the last else statement is
performed. If there is no final else and all other conditions are false then no
action will take place.
Example
// Demonstration of if-else-if ladder
#include <iostream.h>
main ( )
{
int x;
cout << "Enter an integer between 1 and 6";
cin >> x;
if(x==1) cout<<"The number is one  n";
n";
else if(x==2)cout<<"The number is two  n";
n";
else if(x==3)cout<<"The number is three  n";
n";
else if(x==4)cout<<"The number is four  n";
n";
else if(x==5)cout<<"The number is five 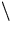 n";
n";
else if(x==6)cout<<"The number is six 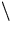 n";
n";
else cout <<"You didn't follow the rules";
return 0;
}
Yousef Haik
2/23/1998
