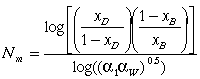
The theoretical minimum number of stages is the number of stages needed to reach a desired separation. The theoretical number of stages at total reflux may be calculated using the Fenske Equation and the McCabe Thiele Model.
The Fenske equation may be used to calculate the theoretical minimum number of stages, Nm, at total reflux for a distillation column with a total condenser.
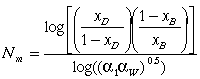
XD=mole fraction of desired product in distillate
XB= mole fraction of desired product in bottoms
a1 = relative volatility of the overhead vapor
aw= relative volatility of the bottoms liquid
McCabe Thiele Model
The McCabe Thiele model may also be used to determine the number of theoretical stages at total reflux. The following steps will enable one to determine the number of stages:
Draw the equilibrium line on an x-y plot.
Draw the y=x line.
Plot the measured bottoms and distillate ethanol mole fractions along the y = x line. For total reflux this line will be your operating line.
Draw a horizontal line from the distillate mole fraction on the operating line to the equilibrium line, followed by a vertical line drawn back down to the operating line. Repeat this until the desired bottoms composition is reached.
Count the number of times the horizontal line hits the equilibrium line to get the number of stages. Note: The last stage is the reboiler.