PEM Fuel Cell - Components
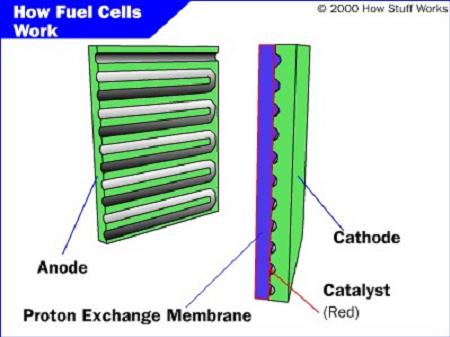
Anode — negative post of fuel cell
![]() Conducts the electrons freed from hydrogen molecules so they can
be used in an external circuit
Conducts the electrons freed from hydrogen molecules so they can
be used in an external circuit
PEM Fuel Cell - Components

Anode — negative post of fuel cell
![]() Conducts the electrons freed from hydrogen molecules so they can
be used in an external circuit
Conducts the electrons freed from hydrogen molecules so they can
be used in an external circuit
![]() Disperses the hydrogen gas equally over the surface of the
catalyst through etched channels
Disperses the hydrogen gas equally over the surface of the
catalyst through etched channels
Cathode — positive post of fuel cell
![]() Conducts the electrons back from the external circuit to the
catalyst
Conducts the electrons back from the external circuit to the
catalyst
![]() Electrons are then recombined with hydrogen ions and oxygen
atoms to form water
Electrons are then recombined with hydrogen ions and oxygen
atoms to form water
![]() Disperses oxygen equally over the surface of catalyst through
etched channels
Disperses oxygen equally over the surface of catalyst through
etched channels
Catalyst — special material that facilitates the reaction of oxygen and
hydrogen
![]() Specially treated material that only conducts positively charged
Specially treated material that only conducts positively charged![]() Resembles ordinary kitchen plastic wrap
Resembles ordinary kitchen plastic wrap![]() Membrane blocks electrons, forcing them around the external
circuit
Membrane blocks electrons, forcing them around the external
circuit![]() Typically made of platinum powder very thinly coated onto
carbon paper or cloth
Typically made of platinum powder very thinly coated onto
carbon paper or cloth![]() Rough and porous so that the maximum surface area of the platinum can be
exposed to the hydrogen or oxygen
Rough and porous so that the maximum surface area of the platinum can be
exposed to the hydrogen or oxygen![]() Platinum coated side of the catalyst faces the PEM
Platinum coated side of the catalyst faces the PEM