The product of thrust and flight velocity, (T * U), is sometimes called thrust power. One measure of the performance of an engine is the ratio of this thrust power to the rate of production of propellant kinetic energy. This ratio is commonly known as the "propulsion efficiency", Np. It is given by the equation
Np = T * U / (ma [(1+f)(Ue^2/2) - U^2/2])
where T is thrust, U is flight velocity, ma is the mass flow rate of air, and Ue is the average exit velocity of that air. If it is assumed that f << 1 and that T is approximately equal to ma * (Ue - U), the equation for propulsion efficiency can be simplified as follows:
Np = 2U / (Ue + U)
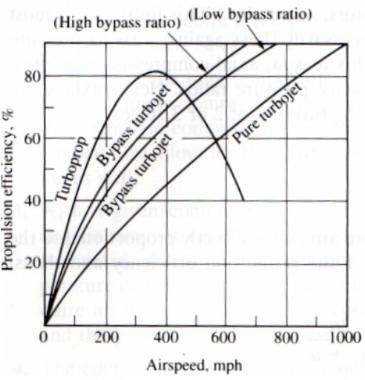
With this in mind, the following chart displays some typical propulsion efficiencies versus airspeed for turbofan, turboprop, and turbojet engines currently in use.
