 |
 |
 |
 |
| RAID
Level: |
[
0 ] |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
10 |
53 |
0+1 |
next |
RAID 0: Striped Disk Array without Fault Tolerance 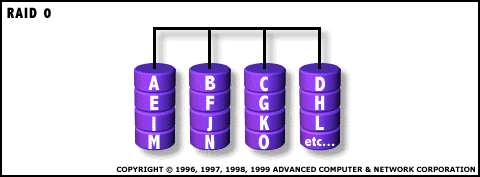 RAID Level 0 requires a
minimum of 2 drives to implement |
RAID 1: Mirroring and Duplexing 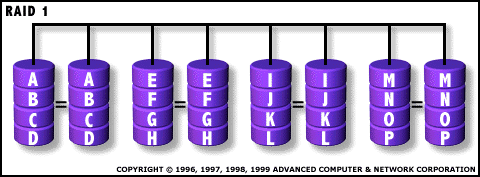 For Highest performance, the
controller must be able to perform two concurrent separate Reads per
mirrored pair or two duplicate Writes per mirrored pair. RAID Level 1 requires a minimum of 2 drives to implement |
RAID
2: Hamming Code ECC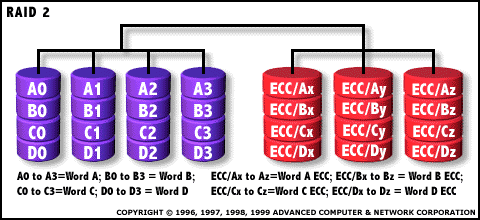 Each bit of data word is
written to a data disk drive (4 in this example: 0 to 3). Each data word
has its Hamming Code ECC word recorded on the ECC disks. On Read, the
ECC code verifies correct data or corrects single disk errors. |
RAID 3: Parallel transfer with parity 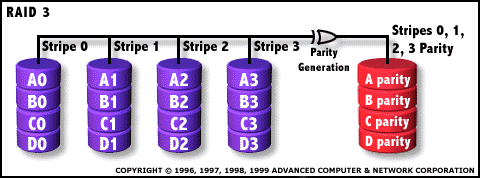 The data block is subdivided
("striped") and written on the data disks. Stripe parity is
generated on Writes, recorded on the parity disk and checked on Reads. RAID Level 3 requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement |
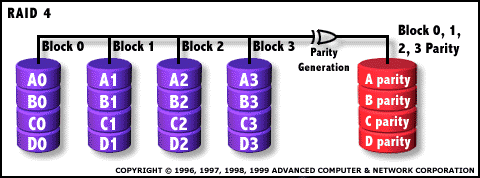
RAID 4: Independent Data disks with shared Parity disk  Each entire block is written
onto a data disk. Parity for same rank blocks is generated on Writes,
recorded on the parity disk and checked on Reads. RAID Level 4 requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement |
RAID 5: Independent Data disks with distributed parity blocks 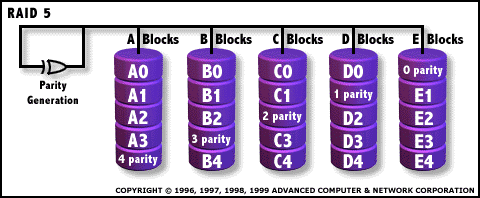 Each entire data block is
written on a data disk; parity for blocks in the same rank is generated
on Writes, recorded in a distributed location and checked on Reads. RAID Level 5 requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement |
RAID
6: Independent Data disks with two independent distributed parity
schemes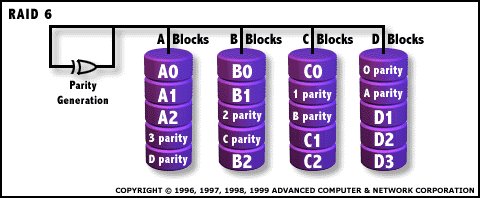 |
RAID 7: Optimized Asynchrony for High I/O Rates as well as High Data Transfer Rates 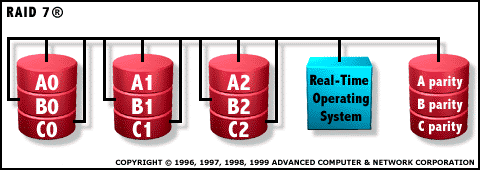 Architectural Features: |
RAID 10: Very High Reliability combined with High Performance 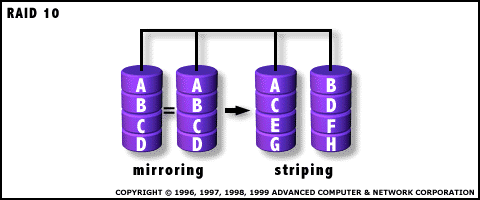 RAID Level 10 requires a
minimum of 4 drives to implement |
¡@
RAID 53: High I/O Rates and Data Transfer Performance  RAID Level 53 requires a
minimum of 5 drives to implement |
RAID 0+1: High Data Transfer Performance  RAID Level 0+1 requires a
minimum of 4 drives to implement |