Inherited system
Inherited Tri-generation Prototype
The tri-generation system inherited achieves its objective of producing heat, refrigeration and electri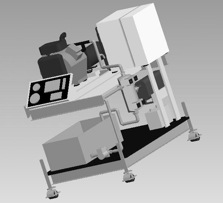
 city from a single source an internal combustion engine. The entire system is composed of four main subsystems. An internal combustion engine, a generator, a water-heating unit and a refrigeration unit. Each of the four subsystems are discussed below.
city from a single source an internal combustion engine. The entire system is composed of four main subsystems. An internal combustion engine, a generator, a water-heating unit and a refrigeration unit. Each of the four subsystems are discussed below.


Internal Combustion Engine (Power Source)
The p
 ower source is a Kawasaki FD501D 16 hp liquid-cooled engine. This delivers the exhaust gas that powers the refrigeration unit and the water-heating unit. The engine is coupled to a generator the provide electrical power. The exhaust gas heat is transferred to other subsystems via 1” nominal type L copper tubing.
ower source is a Kawasaki FD501D 16 hp liquid-cooled engine. This delivers the exhaust gas that powers the refrigeration unit and the water-heating unit. The engine is coupled to a generator the provide electrical power. The exhaust gas heat is transferred to other subsystems via 1” nominal type L copper tubing.


Generator


Refrigeration Unit

Water-Heating Unit
The water-heating unit consists of a 
 20 galloon water reservoir made from reinforced fiberglass. The heat is transferred from the exhaust gas to the water by a Polar Power Inc. Model 30 exhaust heat exchanger.
20 galloon water reservoir made from reinforced fiberglass. The heat is transferred from the exhaust gas to the water by a Polar Power Inc. Model 30 exhaust heat exchanger.


Water Reservoir
History



Tri-generation System
A system that concurrently produces heating, cooling and power from a single source.
Major System Components
-
 Internal Combustion Engine
Internal Combustion Engine -
 Absorption Refrigerator
Absorption Refrigerator -
 Water-heating Unit
Water-heating Unit -
 Generator
Generator
Cogeneration
Also called CHP (combined heat and power) uses a single source to provide heat and power.
