| Analysis in Mechanical Engineering |
|
© Leon van Dommelen |
|
5.1 Introduction
Combined changes in variables are common. For example:
- Error estimates.
- Changes for a moving particle in a field.
- Changes in scalar quantities depending on several variables,
- ...
The key concept is the total differential. For any function
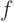

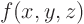 ,
,
Of course, 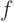 could be a vector.
could be a vector.
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
,